Documentation Generated Automatically
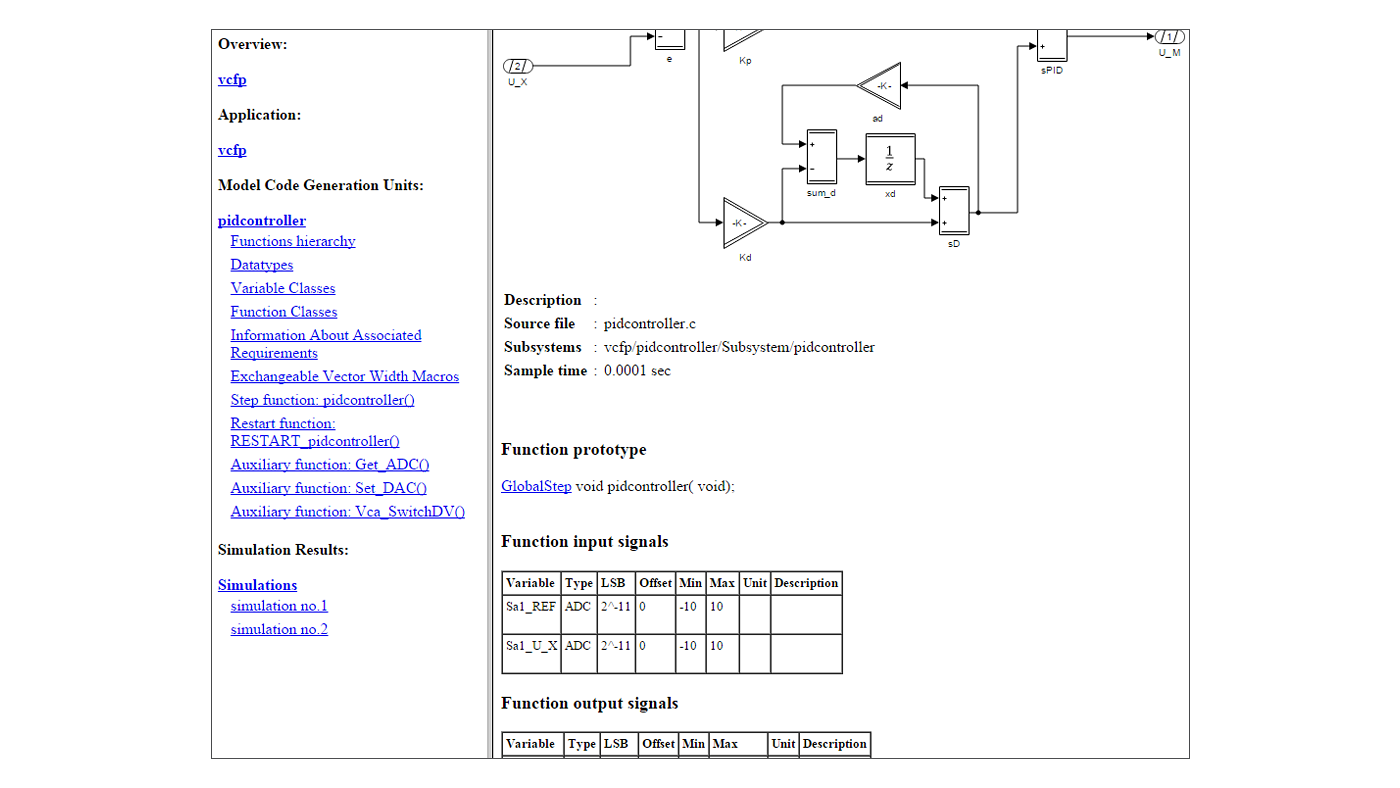
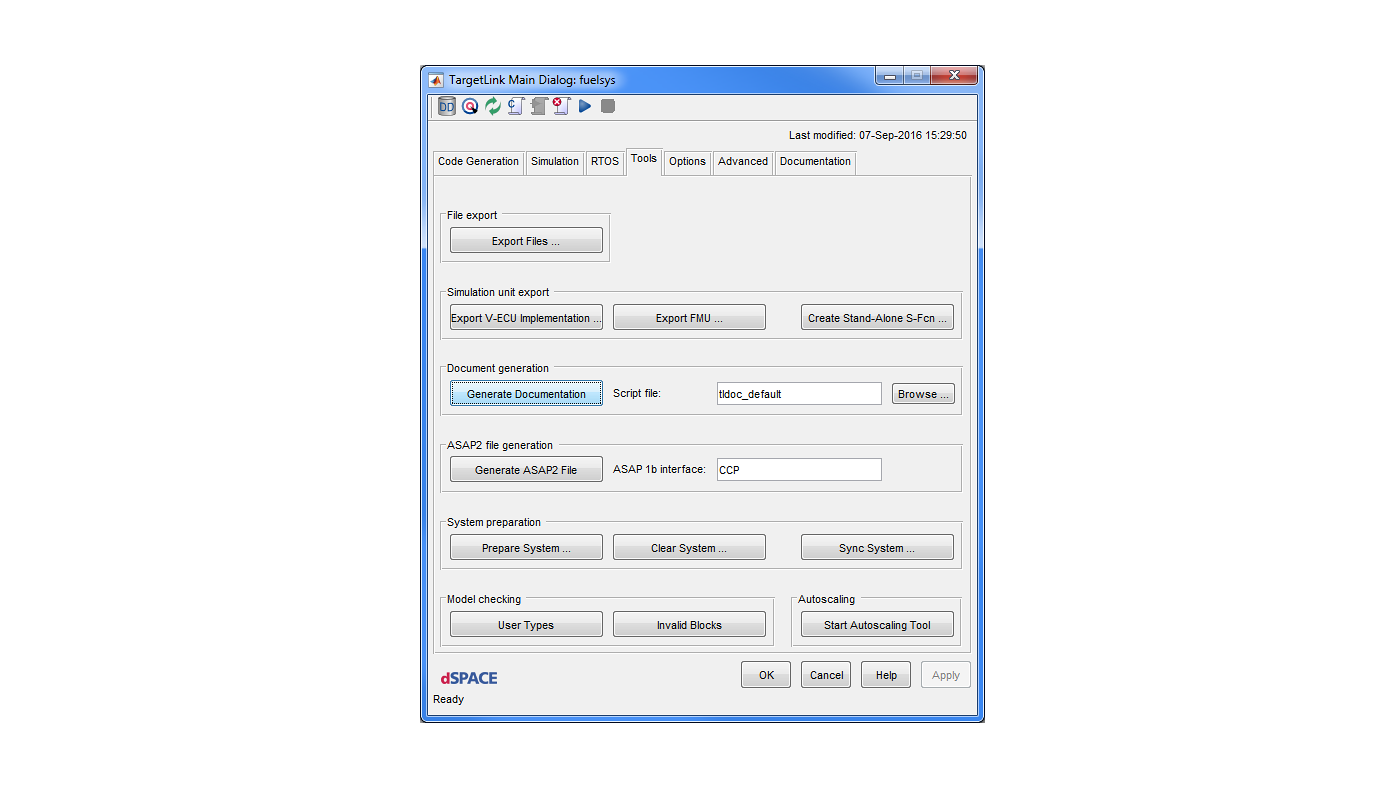
TargetLink not only generates code, it also documents what it does – keeping perfect consistency with the model and the code. An automatically generated document provides information about function interfaces and global variables, and a list of all measurable and adjustable variables, scaling parameters, code generator options and much more.
Screenshots of models, subsystems, and simulation plots can also be included. Links to the generated C code are provided. You can specify the documentation you require, for example, the level of detail. Documentation can be generated in the HTML, RTF (for word processing) and PDF formats.

TargetLinkが機能安全規格ISO 26262、ISO 25119およびIEC 61508の認証を取得
TargetLinkは、TÜV SÜD社(ドイツの第三者試験認証機関)により、安全関連システムの開発ツールとして認定されています。TÜV 社は、ISO DIS 25119、IEC 61508、およびその派生規格(鉄道関連の安全関連ソフトウェアを規定するEN 50128など)に準拠するソフトウェア開発にTargetLinkが適合していることを認定しました。認証は、以下の多数の分野に基づいています。
- TargetLinkのソフトウェア開発プロセスおよびソフトウェア変更プロセス
- 問題の処理手順
- ISO 26262、ISO 25119およびIEC 61508準拠の安全関連開発用途への適合性
TÜV SÜD社はまた、TargetLinkを使用して安全関連ソフトウェアのモデルベース開発を行うための手引となるリファレンスワークフローを承認しました。IEC 61508は、国際的に認知された、安全関連の電子システム開発の汎用規格です。ISO 26262は、安全関連の車載システム開発における国際的な自動車規格です。ISO 25119は、農林用トラクタおよび機械類の制御システムの安全関連部品を開発するうえでの国際規格です。両者はIEC 61508の派生規格です。

TargetLinkとDO-178C/DO-331について
- 上位要件を仕様化するためのSimulink ® /TargetLinkモデル
- 下位要件を仕様化するためのTargetLink設計モデル
- 高品質で読みやすく、かつ追跡可能なソースコードをTargetLinkモデルから生成
- 確立されたMIL/SIL/PIL検証コンセプトによるモデルおよびコードの総合的なシミュレーションサポート
- BTC Embedded Systemツールを含む強力なツールチェーンにより、要件の仕様、テストベクトルの自動生成、要件検証、およびモデルチェックによる形式検証を実行
Overview of TargetLink Certifications & Standards
TargetLink is certified by TÜV SÜD (German international certification association) for use in the development of safety-related systems. TÜV confirmed that TargetLink is suitable for software development according to ISO 26262, ISO 25119, IEC 61508, and derivative standards (such as EN 50128, which governs safety-related software on the railways). The certification was based on a number of areas:
- Software development process and software modification process of TargetLink
- Problem handling procedures
- Fitness for purpose in safety-related development according to ISO 26262, ISO 25119, and IEC 61508
TÜV SÜD also approved a reference workflow providing guidance for the model-based development of safety-related software with TargetLink. IEC 61508 is the internationally recognized generic standard for the development of safety-related electronic systems. ISO 26262 is the international automotive standard for the development of safety-related systems in road vehicles. ISO 25119 is the international standard for the development of safety-related parts of control systems in tractors and machinery for agriculture and forestry. Both standards are derived from IEC 61508.
| Certification/ Standard | Description |
| ISO/IEC 15504 | ISO/IEC 15504 (also known as SPICE: Software Process Improvement and Capability Determination) is an international standard for software processes. Its underlying concept is that a mature software product requires a mature development process. dSPACE has dedicated itself to an ISO/IEC 15504-compliant development process. |
| An internal quality department, the dSPACE quality management team, proactively manages software quality at dSPACE. The team leads software improvement activities, sets internal standards, conducts internal assessments, and provides consultation services to all software groups. It acts independently and ensures that the highest product quality goals are consistently achieved and sustained. | |
| Internal Software Quality Management | An internal quality department, the dSPACE quality management team, proactively manages software quality at dSPACE. The team leads software improvement activities, sets internal standards, conducts internal assessments, and provides consultation services to all software groups. It acts independently and ensures that the highest product quality goals are consistently achieved and sustained. |
| AUTOSAR | As a de-facto standard for automotive E/E architectures, AUTOSAR contains specifications for communication interfaces between application functions and basic system functions. The TargetLink AUTOSAR Module makes TargetLink’s modeling, simulation and code generation features available for designing Classic AUTOSAR software components (SWCs). Furthermore, TargetLink 5.0 supports select features of Adaptive AUTOSAR Release 19-03. AUTOSAR Adaptive Platform, also called Adaptive AUTOSAR, is a standard based on a service-oriented architecture that aims at on-demand software updates and high-end functionalities. |
| FMI | The Functional Mock-up Interface (FMI) is an open standard for the tool-independent exchange and integration of plant models that are provided by various tool vendors. Functional Mockup Units (FMUs) can be exported from TargetLink to simulation environments that support FMI. |
| ASAM MCD-2 MC (ASAP2) | Internal ECU variables in measurement and calibration can be defined in the description format ASAM MCD-2 MC. Because a code generator also needs to have close links with calibration systems, TargetLink can export calibration data as ASAM-MCD 2MC file for calibration tools. |
| MISRA C | The British MISRA C standard (MISRA: Motor Industry Software Reliability Association; www.misra.org.uk) is a widely accepted C subset for projects in the automotive industry. Its aim is to define rules for avoiding common software errors that can occur when software engineers write software by hand. Most of these rules also make sense for machine-generated code. TargetLink-generated code complies with the vast majority of MISRA C rules. If deviations from the MISRA C standard are a technical necessity, they are identified and well documented. dSPACE provides detailed documentation about TargetLink’s MISRA C compliance to all TargetLink customers on request. |
| DO-178C/DO-331 | With the DO-178C as a highly relevant standard for the development of software in aviation, model-based design and automatic code generation has a solid base for use in the aerospace sector. The document DO-331, Model-Based Development and Verification Supplement to DO-178C and DO-278A, which is also part of the standard, was written specifically for this. dSPACE takes this into account by providing a workflow document that explains how to use TargetLink in a model-based tool chain for DO-178C-compliant projects. The workflow document describes how to meet the individual requirements or objectives of DO-178C/DO-331. It focuses not only on TargetLink itself but also on a complete model-based tool chain that can contain further third-party tools, for example, from TargetLink cooperation partners such as BTC Embedded Systems, AbsInt, and Model Engineering Solutions. The workflow document is thus an important contribution towards simplifying the certification of TargetLink-generated code in DO-178C-compliant applications, addressing all criticality levels up to Level A. |