Documentation Generated Automatically
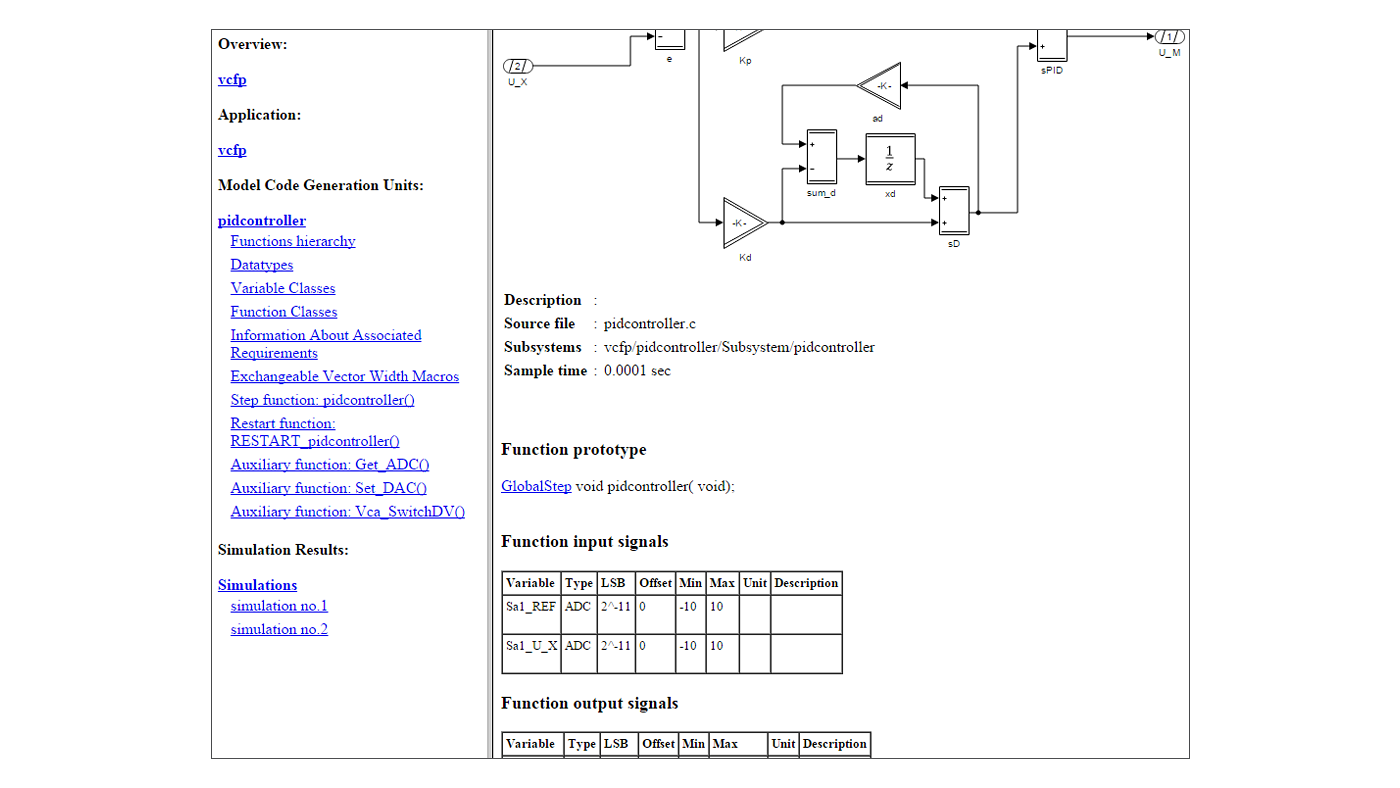
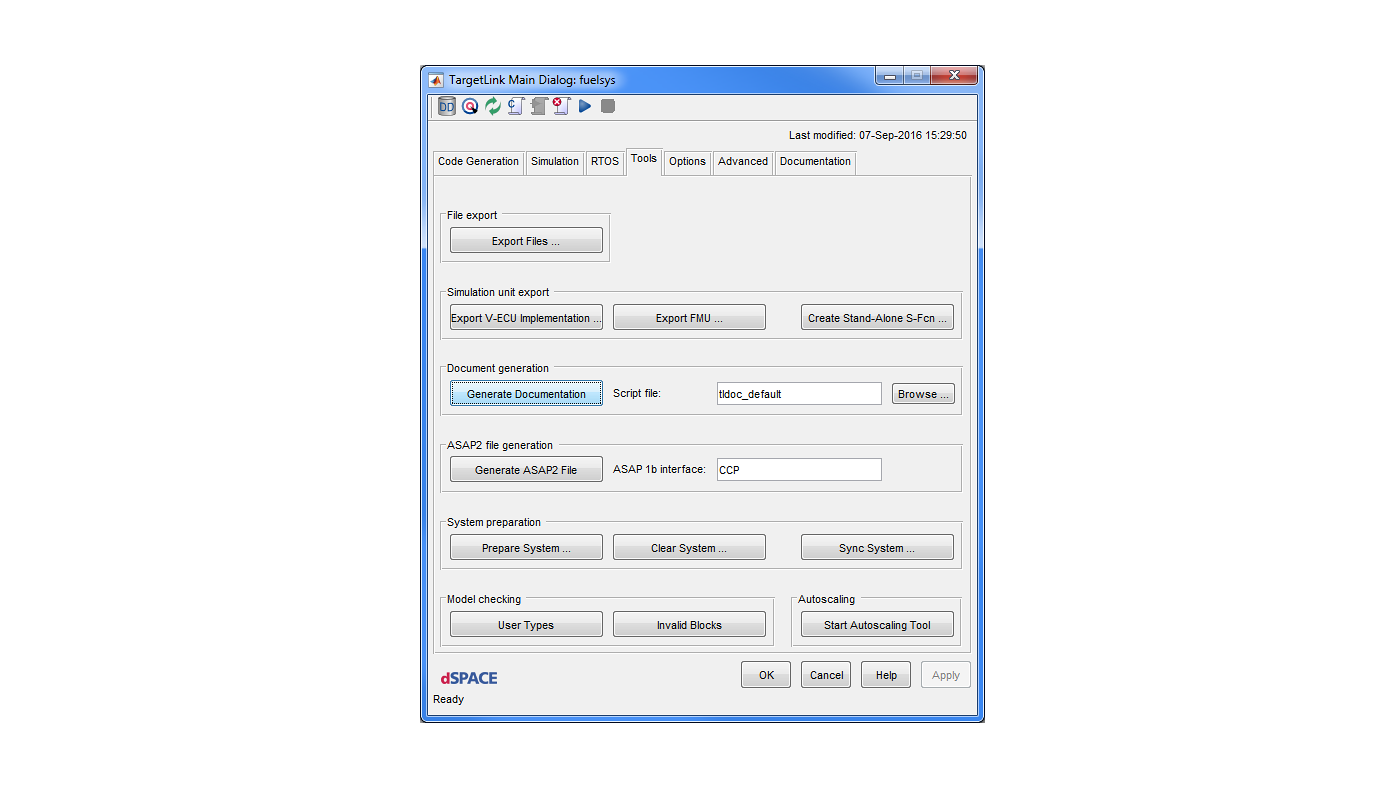
TargetLink not only generates code, it also documents what it does – keeping perfect consistency with the model and the code. An automatically generated document provides information about function interfaces and global variables, and a list of all measurable and adjustable variables, scaling parameters, code generator options and much more.
Screenshots of models, subsystems, and simulation plots can also be included. Links to the generated C code are provided. You can specify the documentation you require, for example, the level of detail. Documentation can be generated in the HTML, RTF (for word processing) and PDF formats.

TargetLink已通过ISO 26262、ISO 25119和IEC 61508认证
TargetLink通过了TÜV SÜD(德国国际认证机构)的认证,可用在安全相关系统的开发应用中。根据 ISO DIS 25119 、ISO 25119、IEC 61508 和衍生标准(例如规定了铁路安全相关软件的 EN 50128),TÜV 证实了 TargetLink 适用于软件开发。认证基于几个方面:
- TargetLink 软件的开发过程和修改过程
- 问题处理步骤
- 根据 IEC 26262 ,ISO 25119和 ISO DIS 61508,证实了其适用于安全相关开发
TÜV SÜD 批准了一项参考工作流程,该流程为使用 TargetLink 进行基于模型的安全相关软件开发提供了指导。IEC 61508 是国际公认的安全相关电子系统开发的通用标准。ISO 26262是道路车辆安全相关系统的国际性汽车标准。ISO 25119也是一项国际标准,其可用于评估农业和林业拖拉机和其他机械控制系统中安全相关组件的开发。这两个标准都是从IEC 61508衍生出来的。

TargetLink和DO-178C/DO-331概况
- 用于指定高级别要求的Simulink ® /TargetLink模型
- 用于指定低级别要求TargetLink 设计模型
- 使用 TargetLink 模型生成高质量、易读、可跟踪的源代码
- 按照现有的 MIL/SIL/PIL 验证概念为模型和代码提供全面的仿真支持
- 强大的工具链含有 BTC Embedded Systems 提供的各种工具,用于实现要求规格、自动测试矢量生成、通过模型检查进行要求验证和格式验证
Overview of TargetLink Certifications & Standards
TargetLink is certified by TÜV SÜD (German international certification association) for use in the development of safety-related systems. TÜV confirmed that TargetLink is suitable for software development according to ISO 26262, ISO 25119, IEC 61508, and derivative standards (such as EN 50128, which governs safety-related software on the railways). The certification was based on a number of areas:
- Software development process and software modification process of TargetLink
- Problem handling procedures
- Fitness for purpose in safety-related development according to ISO 26262, ISO 25119, and IEC 61508
TÜV SÜD also approved a reference workflow providing guidance for the model-based development of safety-related software with TargetLink. IEC 61508 is the internationally recognized generic standard for the development of safety-related electronic systems. ISO 26262 is the international automotive standard for the development of safety-related systems in road vehicles. ISO 25119 is the international standard for the development of safety-related parts of control systems in tractors and machinery for agriculture and forestry. Both standards are derived from IEC 61508.
| Certification/ Standard | Description |
| ISO/IEC 15504 | ISO/IEC 15504 (also known as SPICE: Software Process Improvement and Capability Determination) is an international standard for software processes. Its underlying concept is that a mature software product requires a mature development process. dSPACE has dedicated itself to an ISO/IEC 15504-compliant development process. |
| An internal quality department, the dSPACE quality management team, proactively manages software quality at dSPACE. The team leads software improvement activities, sets internal standards, conducts internal assessments, and provides consultation services to all software groups. It acts independently and ensures that the highest product quality goals are consistently achieved and sustained. | |
| Internal Software Quality Management | An internal quality department, the dSPACE quality management team, proactively manages software quality at dSPACE. The team leads software improvement activities, sets internal standards, conducts internal assessments, and provides consultation services to all software groups. It acts independently and ensures that the highest product quality goals are consistently achieved and sustained. |
| AUTOSAR | As a de-facto standard for automotive E/E architectures, AUTOSAR contains specifications for communication interfaces between application functions and basic system functions. The TargetLink AUTOSAR Module makes TargetLink’s modeling, simulation and code generation features available for designing Classic AUTOSAR software components (SWCs). Furthermore, TargetLink 5.0 supports select features of Adaptive AUTOSAR Release 19-03. AUTOSAR Adaptive Platform, also called Adaptive AUTOSAR, is a standard based on a service-oriented architecture that aims at on-demand software updates and high-end functionalities. |
| FMI | The Functional Mock-up Interface (FMI) is an open standard for the tool-independent exchange and integration of plant models that are provided by various tool vendors. Functional Mockup Units (FMUs) can be exported from TargetLink to simulation environments that support FMI. |
| ASAM MCD-2 MC (ASAP2) | Internal ECU variables in measurement and calibration can be defined in the description format ASAM MCD-2 MC. Because a code generator also needs to have close links with calibration systems, TargetLink can export calibration data as ASAM-MCD 2MC file for calibration tools. |
| MISRA C | The British MISRA C standard (MISRA: Motor Industry Software Reliability Association; www.misra.org.uk) is a widely accepted C subset for projects in the automotive industry. Its aim is to define rules for avoiding common software errors that can occur when software engineers write software by hand. Most of these rules also make sense for machine-generated code. TargetLink-generated code complies with the vast majority of MISRA C rules. If deviations from the MISRA C standard are a technical necessity, they are identified and well documented. dSPACE provides detailed documentation about TargetLink’s MISRA C compliance to all TargetLink customers on request. |
| DO-178C/DO-331 | With the DO-178C as a highly relevant standard for the development of software in aviation, model-based design and automatic code generation has a solid base for use in the aerospace sector. The document DO-331, Model-Based Development and Verification Supplement to DO-178C and DO-278A, which is also part of the standard, was written specifically for this. dSPACE takes this into account by providing a workflow document that explains how to use TargetLink in a model-based tool chain for DO-178C-compliant projects. The workflow document describes how to meet the individual requirements or objectives of DO-178C/DO-331. It focuses not only on TargetLink itself but also on a complete model-based tool chain that can contain further third-party tools, for example, from TargetLink cooperation partners such as BTC Embedded Systems, AbsInt, and Model Engineering Solutions. The workflow document is thus an important contribution towards simplifying the certification of TargetLink-generated code in DO-178C-compliant applications, addressing all criticality levels up to Level A. |