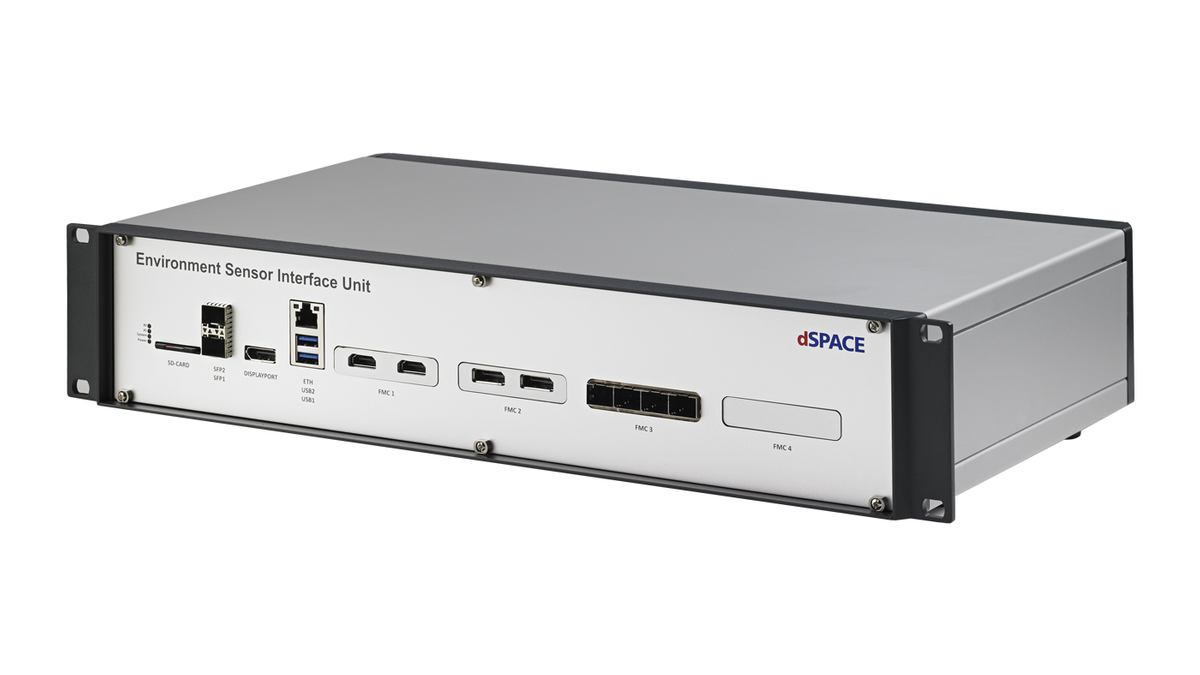
Environment Sensor Interface Unit
Feeding digital data into camera, radar and lidar ECUs
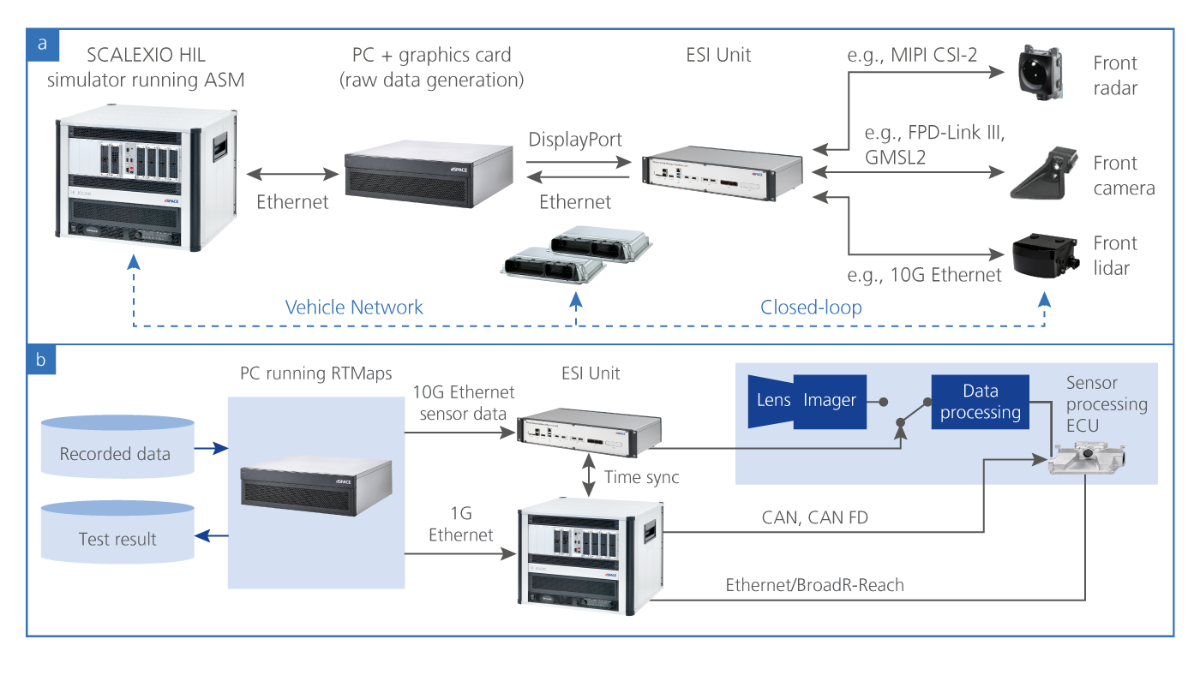
Systems for autonomous driving use multiple environment sensors. To simulate the sensors in a HIL setup for sensor fusion and function testing, it is essential to accurately synchronize the stimulation of the individual sensors. The dSPACE Environment Sensor Interface Unit supports the time-correlated feeding of raw sensor data to one or more sensor ECUs.
-
Preconfigured ESI Units
The Environment Sensor Interface Unit (ESI Unit) from dSPACE allows both real and simulated raw sensor data to be fed into ADAS/AD ECUs in a time-correlated manner. This is extremely useful for HIL tests of functions for autonomous driving, among other things. To make these tests as easy as possible, dSPACE now also offers preconfigured ESI Units for specific, widely used application scenarios:
- ESI Kit YUV: Preconfigured Environment Sensor Inter¬face Unit for YUV camera simulation (GMSL2 or FPD-Link III)
- ESI Kit DRIVE: Preconfigured Environment Sensor Inter¬face Unit for NVIDIA® DRIVE AGX
- High-performance FPGA for feeding raw sensor data to sensor ECUs in a synchronized manner
- Flexible adaption of long- and short-range raw data interfaces, including FPGA-based sensor models
- Support for ADI/Maxim GMSL1/2/3, TI FPD-Link III/IV, Sony GVIF2/3, and MIPI CSI-2 D-PHY
- Simulation of up to 12 sensors with 50 Gbit/s of aggregated bandwidth
Application Areas
For the development and validation of environment sensors, e.g., radar, camera and lidar, and more generally the validation of ADAS/AD functions, support for a range of ECU interfaces for data insertion is essential. In addition to testing based on over-the-air methods and object lists, the insertion of raw data or target lists is of utmost importance for the validation of perception and fusion algorithms that are based on raw data. The Environment Sensor Interface (ESI) Unit supports all relevant sensor interfaces and is important for closed-loop and open-loop testing. Advanced sensor simulation in combination with the ESI Unit makes it easy to provide synthetic sensor data under realistic conditions and with low latencies. This is useful for validating functions for autonomous driving in HIL simulation (closed- and open-loop). If RTMaps is used as well, recorded sensor data can be replayed conveniently. A major advantage of the ESI Unit is that it can be used to process both data replay and sensor simulation simultaneously or sequentially and on the same HIL simulator.
Key Benefits
The ESI supports the injection of raw data and target lists for HIL tests of camera, radar, and lidar ECUs as well as central processing units for autonomous driving. Thanks to its flexible and scalable architecture, the ESI Unit supports tasks such as lidar point cloud data injection via 10 Gigabit Ethernet, radar raw data injection via MIPI CSI-2 D-PHY, and camera raw data injection via ADI/Maxim GMSL1/2/3, TI FPD-Link III/IV, Sony GVIF2/3, or MIPI A-PHY. To meet the requirements of next-generation ECUs, the ESI Unit can be configured to simulate the latest sensors, including FPGA-based sensor models. A single ESI Unit simulates up to twelve sensors synchronously and supports more than 50 Gbit/s of aggregated bandwidth. Multiple combined ESI Units let you test functions for autonomous driving with dozens of different sensors. Special customer requirements and functions can be implemented directly on the ESI Unit thanks to the powerful Xilinx® UltraScale+™ FPGA.
Preconfigured Environment Sensor Interface Unit
dSPACE offers preconfigured ESI Units for specific, widely used application scenarios. All kits handle the simulation of 4 cameras using synthetic sensor data (with AURELION) and recorded sensor data (with RTMaps):
- ESI Kit YUV: Preconfigured Environment Sensor Interface Unit for YUV camera simulation (GMSL2 or FPD-Link III)
- ESI Kit DRIVE: Preconfigured Environment Sensor Interface Unit for NVIDIA® DRIVE AGX.
| Parameter | Specification |
|---|---|
|
FPGA |
|
|
Memory |
|
| Sensor interfaces |
|
| Input interfaces |
|
| Design |
|
| Cooling |
|
| Power supply |
|
| Weight |
|
| Size |
|
| Camera |
|
| Radar |
|
| Lidar |
|
1) Available on request.
-
- View online
- Download
- Data Logging Our mission is to optimize data logging, enable quick responses to new iterations of training and validation and allow for very short data cycles
- ADAS & Autonomous Driving Open, end-to-end simulation and validation solution to empower safe automated driving
- Use Case: Open-Loop HIL System for Testing Image Processing ECUs Data replay system for testing image processing ECUs
- Use Case: Closed-Loop HIL Testing of Camera Systems Closed-Loop HIL System for Testing Camera-Based Systems by Inserting Data into the Image Sensor Output
- Use Case: Closed-Loop HIL Testing of Multisensor Systems Closed-Loop HIL Testing of Multisensor Systems
Drive innovation forward. Always on the pulse of technology development.
Subscribe to our expert knowledge. Learn from our successful project examples. Keep up to date on simulation and validation. Subscribe to/manage dSPACE direct and aerospace & defense now.